Abstract: Under pressures related to economic growth and environmental protection,
China is facing an increasingly severe “environment–health–poverty” trap risk. Fuel taxation
is generally considered an effective policy to counter such a risk. Since 2009 China has raised
the fuel tax rate many times to enhance tax reform. However, the effects of this policy remain
unknown. Therefore, it is vitally important to estimate the impacts of China’s current fuel
taxation policy on environment, public health and the national economy. As the first attempt
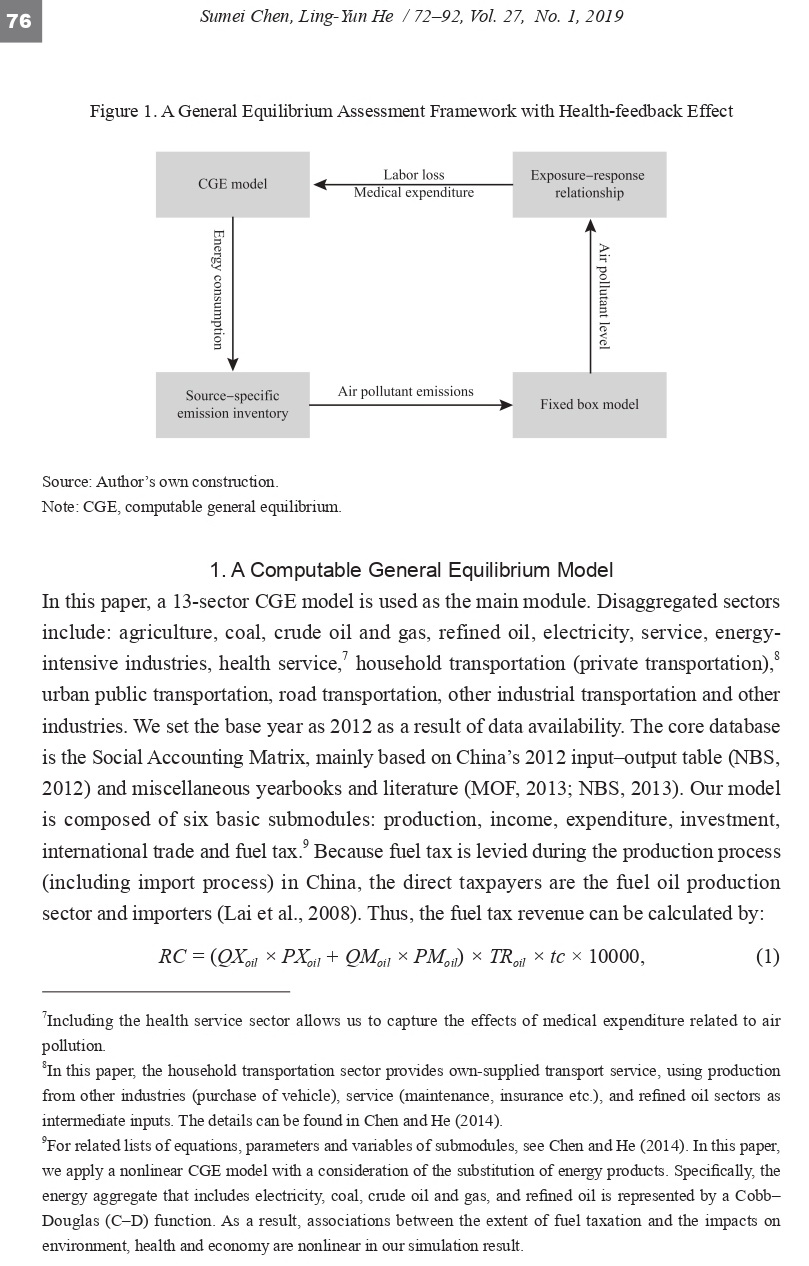
in existing literature on China, this paper builds a general equilibrium framework with the
feedback effect of public health on economy. We find that that the fuel tax policy benefits
the adjustment of the economic structure and improves human health; however, it is
detrimental to economic growth, public welfare and price stability. In this sense, it plays a
limited role in reducing the trap risk and might not be sustainable in the long term.
Key words: economic growth, environment–health–poverty trap, fuel tax, public health




剩余16页
↓下载附件查看PDF全文↓